Free and versatile software solution for chemical maps analysis

EPMA & SEM
LA-ICPMS

CT-scanner

AND MORE

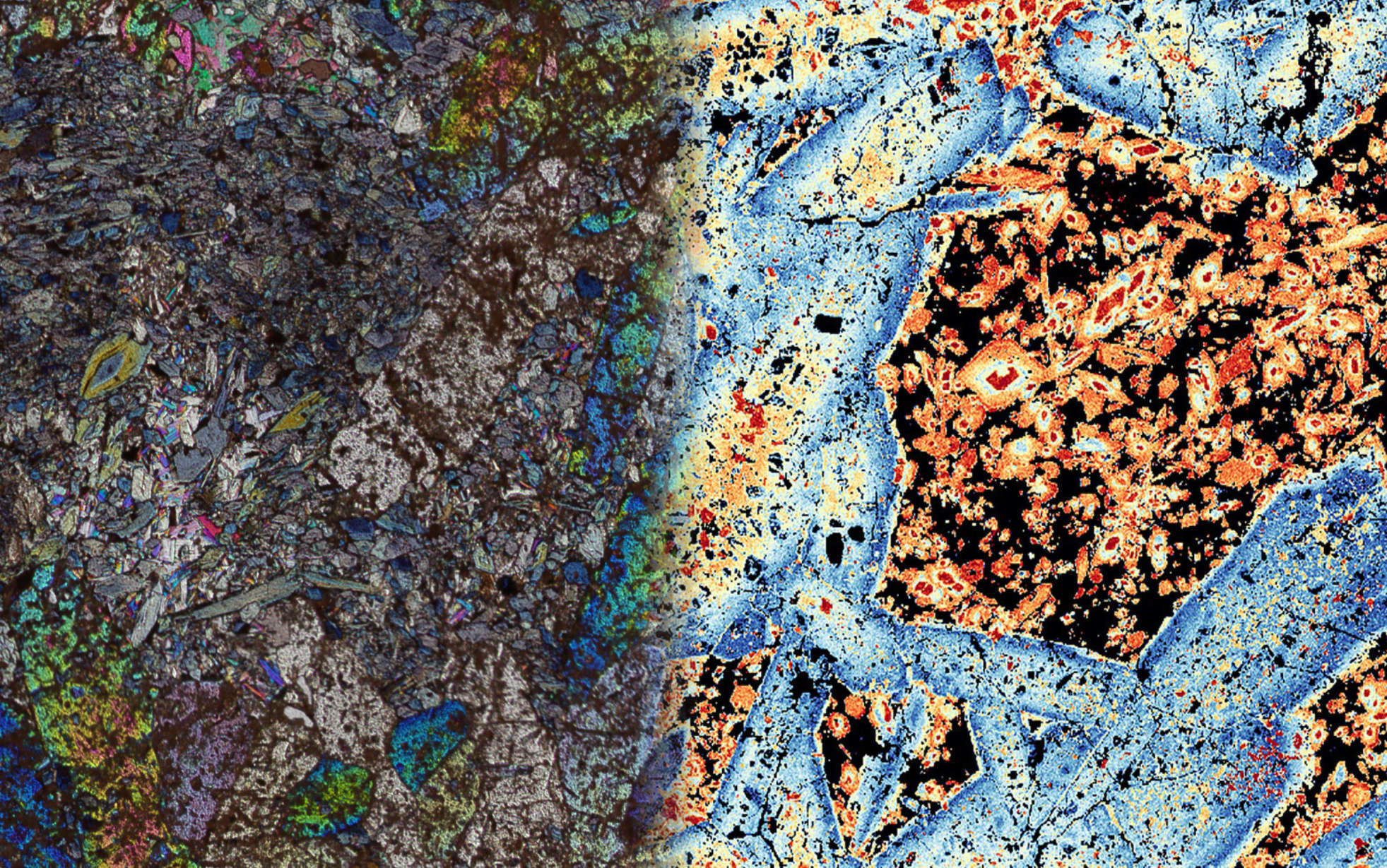
XMapTools is an advanced analysis software for quantitative chemical analysis of solids in 1D, 2D and 3D.
It provides numerical tools and packages implemented in a guided and versatile environment that allows you to explore and visualise data in your own way.
For example, XMapTools includes a wide range of data processing options including routines for classification, segmentation, calibration and visualisation via single and multi-channel maps or via binary, ternary and spider diagrams.
MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS
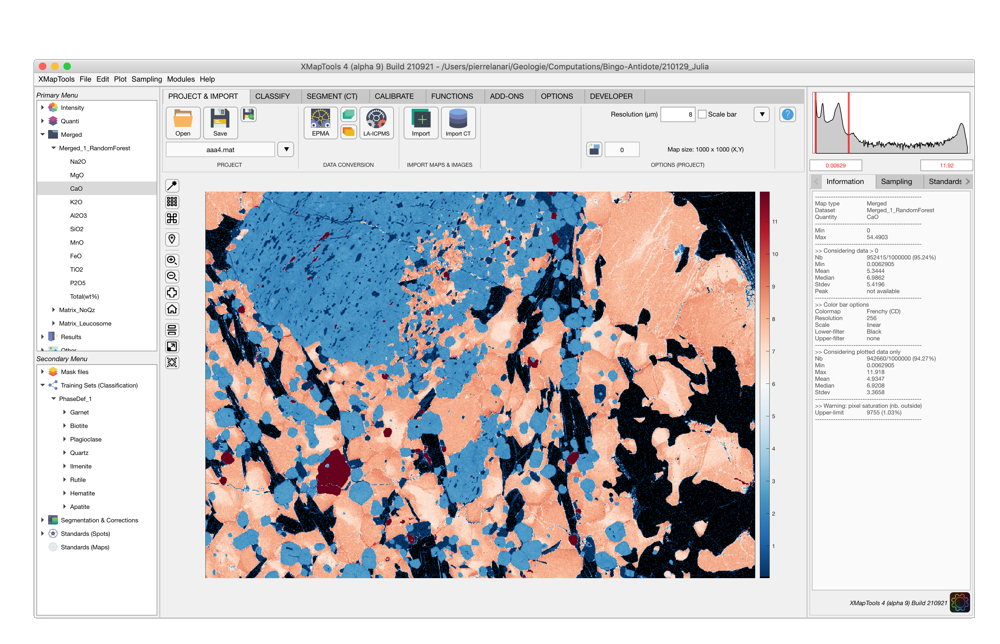
Several machine learning algorithms are available for classification and segmentation of chemical data. Select pixel data to train a new classification model.
SMART DATA CALIBRATION
New dedicated modules are available to guide you through the standardisation of EPMA and LA-ICP-MS data. Data calibration is now faster and more accurate.

ADVANCED DATA EXPLORATION TOOLS
State-of-the-art interaction tools have been implemented to provide a completely new experience for all users. Import your existing project and start exploring your data on a new level.
PETROLOGICAL CALCULATIONS
Discover an expanded range of external functions that can be calculated instantly. This new package contains more functions than ever before.
FEATURES
Machine Learning
Visualisation
Thermobarometry
Simulations
Education
Welcome XMapTools 4.3!

XMapTools 4.3 updates the LA-ICPMS data reduction experience described in the paper by Markmann et al. (2024) and provide improvements in classification and data visualisation.

XMapTools 4.3 (build 240114)
Public version (released January 2024)
XMapTools 4 provides an optimal framework for chemical data analysis and correlative compositional mapping across multiple instruments (e.g. EPMA, LA-ICP-MS, CT-SCANNER, FTIR, etc.). This version of XMapTools is distributed as a standalone application (Mac & Windows) and includes Bingo-Antidote 2. The source code is available on Github.
Free training for users
We are working hard to provide training material for XMapToosl 4. At the moment, you can get help for the main steps of the data processing procedure described in a user guide available in the program.
INTEGRATED USER-GUIDE
XMapTools 4 has an integrated user-guide which can be displayed at any stage of the processing. This is the simplest and quickest way to get access to a description of each part of the program.
RESOURCES WEBSITE
We are building a resources website that will contain articles describing the main steps of data reduction.
VIDEOS
Take a look at the video tutorials that show you the main features of XMapTools. This is the quickest and easiest way to learn how to use the software.
TUTORIAL FOR EPMA DATA (2023)
Follow this step-by-step tutorial to become familiar with the procedure for data reduction of EPMA data and to discover the main features of XMapTools.
Functionalities
Citations
App Downloads
“I really enjoy using XMapTools 4, and I will keep it open the whole day when I work. I quickly standardised my maps of a whole thin section, and found amazing gradients in compositional zoning. Data from LA-ICP-MS or CT-scanner can also be used and calibrated in XMapTools 4. It is really a very powerful and versatile software, and a good friend for petrologists!”
Jiahui, China
“XMapTools 4 comes as a standalone application that is much more stable than previous versions. The mineral classification is better and the selection of various regions-of-interest for each mineral in the training phase reduces the number of mixing pixels.”
Alice, Brazil
“XMapTools 4 greatly speeds up the processing for electron microprobe data. Many functions are applied instantaneously! Visualisation has improved and the program is very user-friendly. Excellent software!”
Qian, China
If you have ideas, join the team!
Anyone can participate in the development of XMapTools via Github